steam() : 把一个源数据,可以是集合,数组,I/O channel, 产生器 generator 等,转化成流。
Collectors() : 类实现了很多归约操作,例如将流转换成集合和聚合元素。通过 stream ().collect () 方法可简单获得我们所需要的数据结构。
先创建一个 prodList 的集合数据
| @Data |
| public class Product { |
| private Long id; |
| private Integer num; |
| private BigDecimal price; |
| private String name; |
| private String category; |
| |
| public Product(Long id, Integer num, BigDecimal price, String name, String category) { |
| this.id = id; |
| this.num = num; |
| this.price = price; |
| this.name = name; |
| this.category = category; |
| } |
| } |
| Product prod1 = new Product(1L, 1, new BigDecimal("15.5"), "面包", "零食"); |
| Product prod2 = new Product(2L, 2, new BigDecimal("20"), "饼干", "零食"); |
| Product prod3 = new Product(3L, 3, new BigDecimal("30"), "月饼", "零食"); |
| Product prod4 = new Product(4L, 3, new BigDecimal("10"), "青岛啤酒", "啤酒"); |
| Product prod5 = new Product(5L, 10, new BigDecimal("15"), "百威啤酒", "啤酒"); |
| List<Product> prodList = Lists.newArrayList(prod1, prod2, prod3, prod4, prod5); |
- 将集合里的某个参数拿出来重新生成一个集合,如下将
prodList 里的 name 参数重新生成一个集合
| List<String> nameList = prodList.stream().map(item -> item.getName()).collect(Collectors.toList()); |
![在这里插入图片描述]()
- 对集合里的数据进行处理,如下将集合里的
青岛啤酒 名称改为 哈尔滨啤酒
| public class test { |
| public static void main(String[] args) { |
| Product prod1 = new Product(1L, 1, new BigDecimal("15.5"), "面包", "零食"); |
| Product prod2 = new Product(2L, 2, new BigDecimal("20"), "饼干", "零食"); |
| Product prod3 = new Product(3L, 3, new BigDecimal("30"), "月饼", "零食"); |
| Product prod4 = new Product(4L, 3, new BigDecimal("10"), "青岛啤酒", "啤酒"); |
| Product prod5 = new Product(5L, 10, new BigDecimal("15"), "百威啤酒", "啤酒"); |
| List<Product> prodList = Lists.newArrayList(prod1, prod2, prod3, prod4, prod5); |
| prodList = prodList.stream().map(T -> setData(T)).collect(Collectors.toList()); |
| for (Product product : prodList) { |
| System.out.println("product="+product); |
| } |
| } |
| |
| private static Product setData(Product t) { |
| if (StringUtils.equals(t.getName(), "青岛啤酒")) { |
| t.setName("哈尔滨啤酒"); |
| } |
| return t; |
| } |
| } |
![在这里插入图片描述]()
- 将集合需要的参数数据转化成
Map ,如下将 id 与 name 转化成 Map
| |
| Map<Long, String> idMap = prodList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Product::getId, Product::getName)); |
| System.out.println("idMap="+idMap); |
![在这里插入图片描述]()
- 将集合通过某个参数进行分组,对组织人员进行部门分组的时候有奇效,如下将对
category 分组
| |
| Map<String, List<Product>> groupListMap = prodList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Product::getCategory)); |
| System.out.println("nameList="+groupListMap); |
| |
| |
| nameList={啤酒=[Product(id=4, num=3, price=10, name=青岛啤酒, category=啤酒), Product(id=5, num=10, price=15, name=百威啤酒, category=啤酒)], |
| 零食=[Product(id=1, num=1, price=15.5, name=面包, category=零食), Product(id=2, num=2, price=20, name=饼干, category=零食), Product(id=3, num=3, price=30, name=月饼, category=零食)]} |
- 将集合通过某个参数进行拼接,如下将
name 进行拼接
| |
| String nameJoin = prodList.stream().map(Product::getName).collect(Collectors.joining(",")); |
| System.out.println("nameJoin="+nameJoin); |
![在这里插入图片描述]()
- 统计集合的总数
| |
| Long count = prodList.stream().collect(Collectors.counting()); |
| System.out.println("count="+count); |
![在这里插入图片描述]()
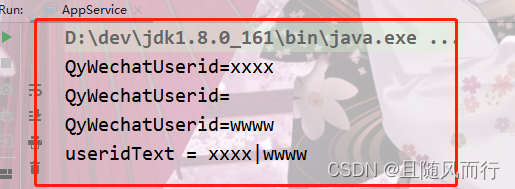
7. 将集合通过某个参数进行拼接(忽略空值) StringUtils.isNotEmpty(s)).collect(Collectors.joining("|")
| public static void main(String[] args) { |
| List<SysAccount> list = new ArrayList<>(); |
| SysAccount sys = new SysAccount(); |
| sys.setQyWechatUserid("xxxx"); |
| list.add(sys); |
| SysAccount sys2 = new SysAccount(); |
| sys2.setQyWechatUserid(""); |
| list.add(sys2); |
| SysAccount sys1 = new SysAccount(); |
| sys1.setQyWechatUserid("wwww"); |
| list.add(sys1); |
| for (SysAccount account : list) { |
| System.out.println("QyWechatUserid="+account.getQyWechatUserid()); |
| } |
| String useridText = list.stream().map(SysAccount::getQyWechatUserid).filter(s -> StringUtils.isNotEmpty(s)).collect(Collectors.joining("|")); |
| System.out.println("useridText = " + useridText); |
| } |
![在这里插入图片描述]()
8. 过滤对象中的空数据字段 .filter(s -> s.getName() != null && StringUtils.isNotBlank(s.getName()))
| List<BeanMap> collect = sysResourceBeans.stream().filter(s -> s.getName() != null && StringUtils.isNotBlank(s.getName())).map(BeanMap::create).collect(Collectors.toList()); |
以上就是我在开发中常用到的 Stream.collect () 方法。